
In this lesson, you will:
- Comprehend the significance of Solidity in the Solana ecosystem.
- Learn about the Solidity program compilation process.
- Differentiate between the Solidity compilation in Ethereum and Solana.
This lesson guides you through the Solidity program compilation process. Solidity
is vital for developing smart contracts on Solana, utilizing the Solang compiler to transform Solidity code into bytecode compatible with Solana. The procedure involves writing in Solidity, compiling to Solana bytecode, deploying on the Solana network, and activating the program. While the core principles of Solidity remain the same, there are nuances in its application on Solana compared to Ethereum. Directly transferring code from Ethereum may require adjustments for optimal functionality on Solana.
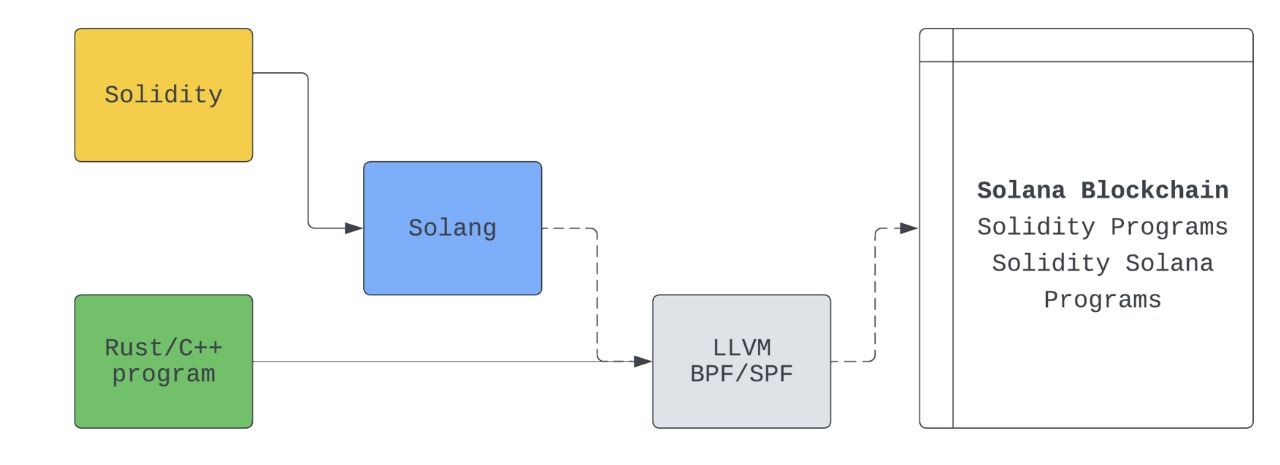
Integrating Solidity with Solana
Solidity plays a crucial role in Solana's blockchain ecosystem. The key to leveraging Solidity on Solana is the Solang compiler, which translates Solidity code into a format compatible with the Solana blockchain. The compiler optimizes the code into bytecode or machine code tailored for Solana, facilitating the creation and deployment of smart contracts on the Solana platform.
The process involves:
- Writing in Solidity: The initial step is crafting smart contracts in Solidity.
- Compilation: Using the Solang compiler, the Solidity code is compiled into BPF (Berkeley Packet Filter) or SBF (Solana Bytecode Format) bytecode, utilizing the LLVM compiler for optimization.
- Deployment: The compiled BPF or SBF bytecode is then deployed on the Solana blockchain, establishing a Solana program.
- Activation: The Solana program, written in Solidity, becomes operational within the Solana network.
Adjustments may be necessary when transitioning Solidity code from Ethereum to Solana, ensuring compatibility and smooth integration with Solana's blockchain.
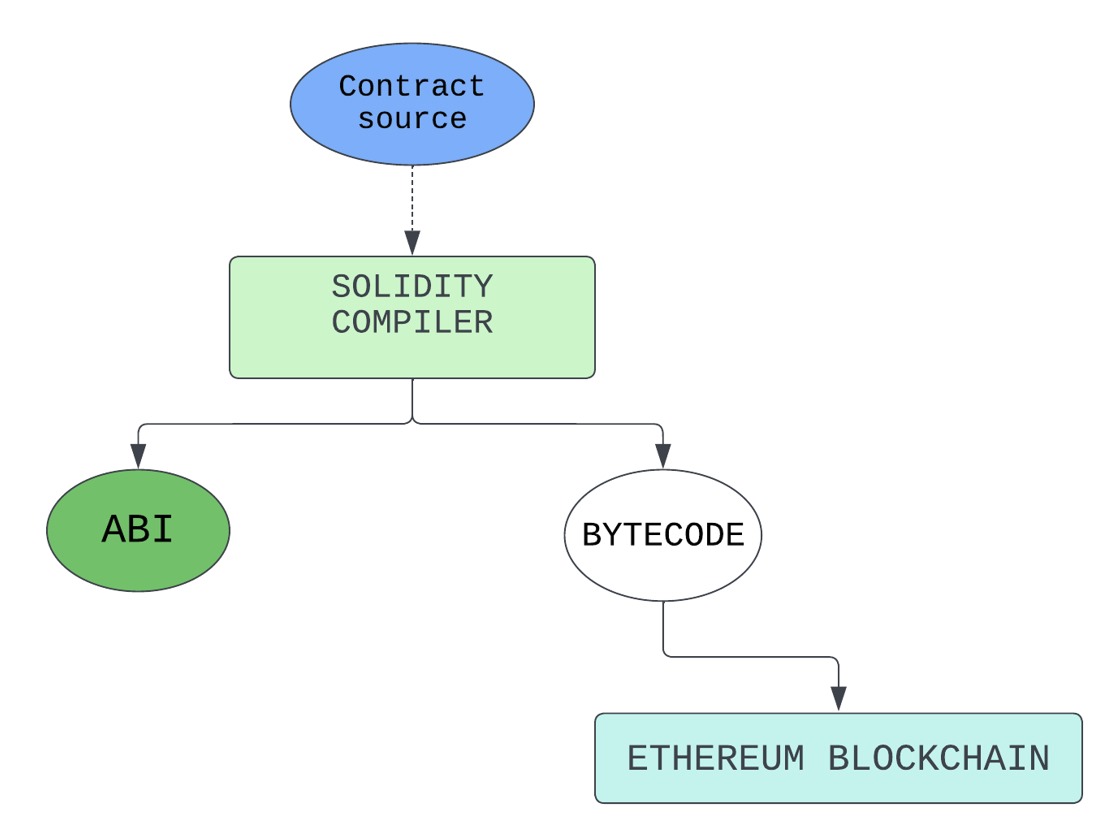
Developing and Deploying Solidity Smart Contracts on Ethereum
The workflow for creating and deploying smart contracts using Solidity on Ethereum typically follows these steps:
- Contract Creation: The process begins by writing a smart contract in Solidity, resulting in a .sol file.
- Compilation: The Solidity compiler is used to compile the smart contract.
- Conversion to ABI and Bytecode: Post-compilation, the code is transformed into ABI (Application Binary Interface) and bytecode, preparing it for integration with the Ethereum network.
- Program Bytecode Formation: The bytecode evolves into program bytecode, an essential phase in the contract development.
- Deployment on Ethereum: The final step is deploying the smart contract onto the Ethereum blockchain, making it operational within the network.
This sequence encapsulates the end-to-end process of implementing a Solidity-based smart contract on Ethereum.
In the next lesson, we will delve deeper into Solang, exploring the Solidity compiler extensively, and understanding how it enables Solidity-based development within the Solana ecosystem. We will examine its functionalities, compatibilities, and the unique features it brings to Solana's development environment.